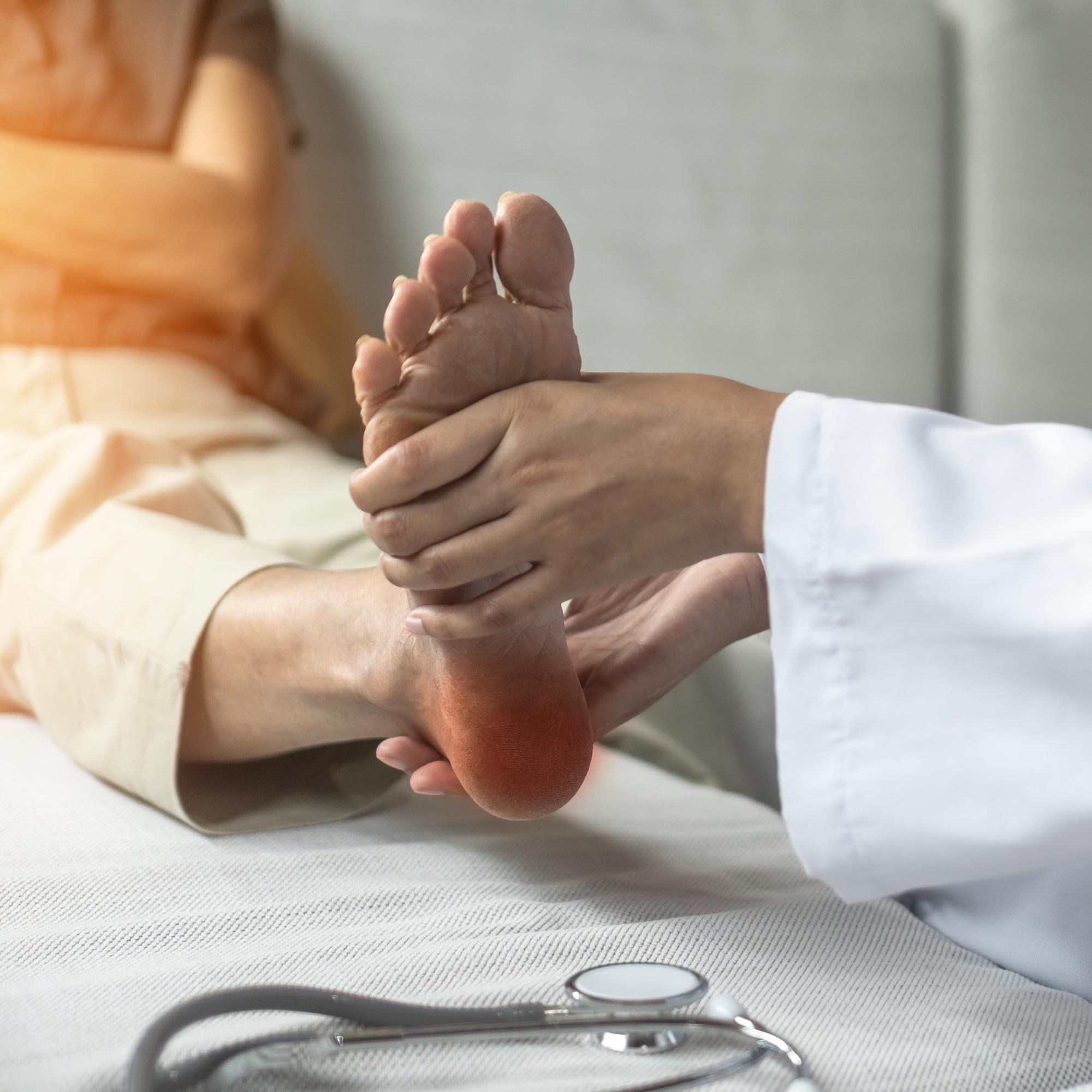
When your feet hurt, your daily activities can become a pain too. Your feet bear much of your weight and do a lot of work every day, so they’re susceptible to many different ailments. Foot pain may affect the top of your foot, the ball of your foot, your arch, or your heel. Here are some of the most common causes of foot pain and how you can address them.
Heel spurs
A heel spur is a bony growth, usually under the heel where it connects to tissue that runs the length of the foot. If the tissue becomes stretched by overuse, ill-fitting shoes, or excess weight, it can become inflamed and pull on the bone. The body reacts to the stress by building extra bone.
Treatment includes:
- Rest and intermittent icing
- Stretching exercises
- Supportive, well-fitting shoes
- Steroid injections
- Surgery in some cases
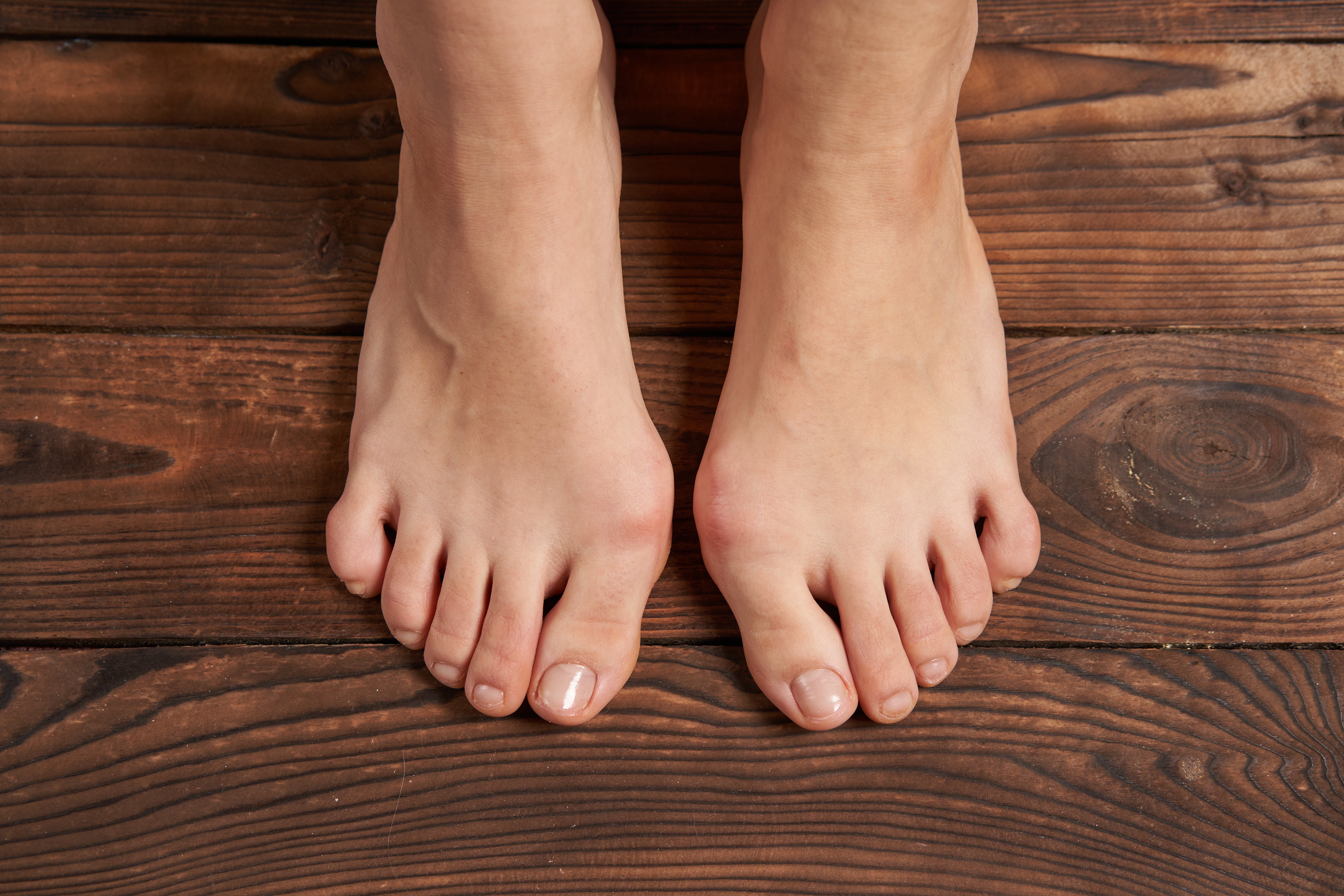
Bunions
A bunion is a hard bump on the bottom joint of the big toe. Bunions form when the toe is pulled toward the rest of the foot, which may be due to tight shoes or the shape of the foot. If a bunion becomes inflamed, it can be sore and tender to the touch. Wear shoes that don’t press on the big toe and keep your toes flexible with stretches. Icing may relieve pain. There are several types of surgery for bunions, but recovery can take months and they may reappear.

Morton's neuroma
When two foot bones rub together and press on the nerves between them, the body may create extra nerve tissue, which is called Morton’s neuroma. It usually develops between the bones leading to the third and fourth toes and tends to occur in people who stand or walk for long periods of time. It can cause swelling, tingling, numbness, tenderness and pain. Treatment includes rest and wearing shoes that allow your feet to move freely. In severe cases, cortisone injections or surgery can help.
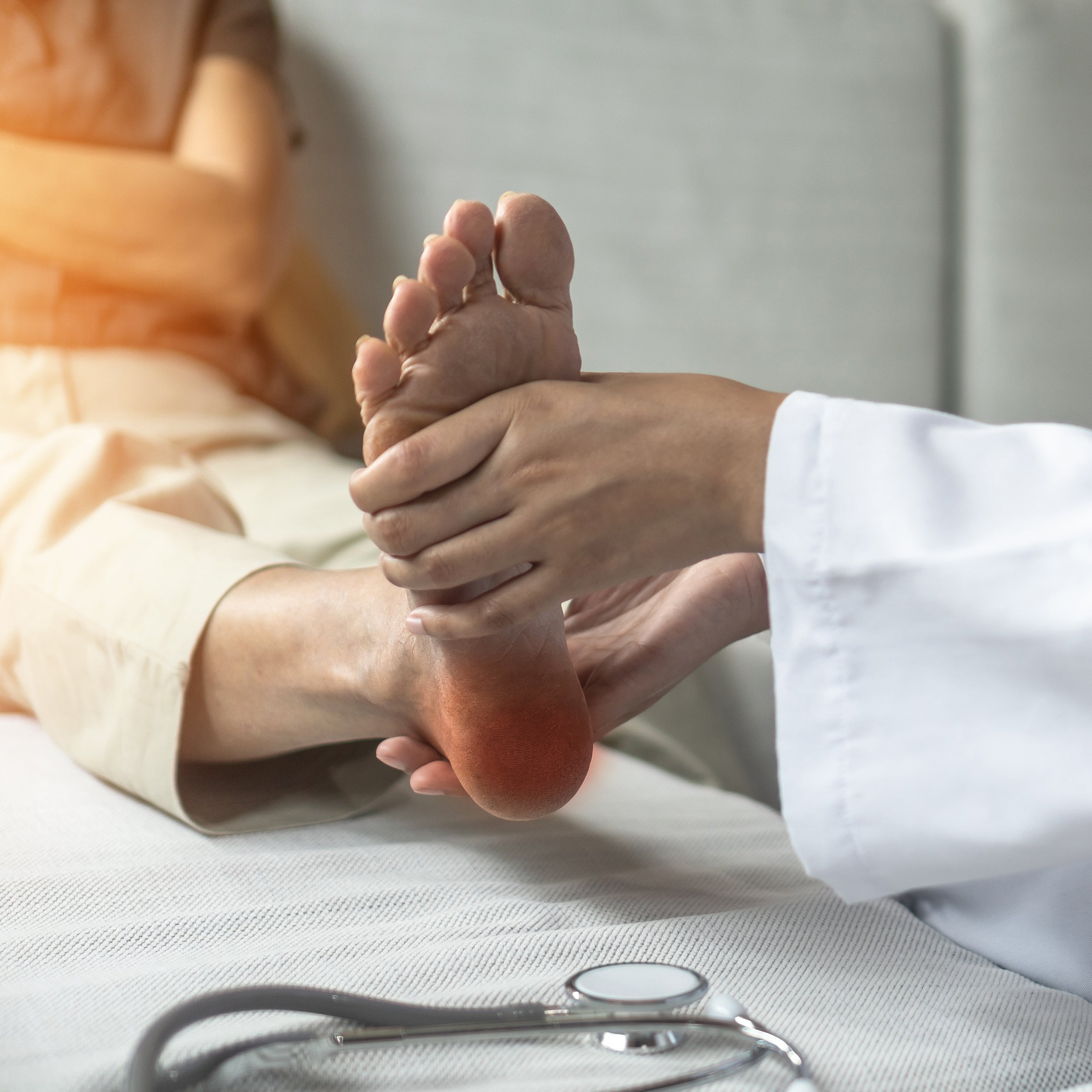
Plantar fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the fibrous tissue (fascia) on the bottom of your foot that connects the heel to the base of the toes. It causes heel pain, especially when you stand up after sitting or lying down for a while. Plantar fasciitis is an overuse injury, more common in women, people who are overweight, people with flat feet or high arches, and those who walk or stand on hard surfaces frequently. If you walk or run without warming up your calves, it can also contribute to the condition. Treatment includes rest, stretches as directed by a healthcare professional, and proper foot support.
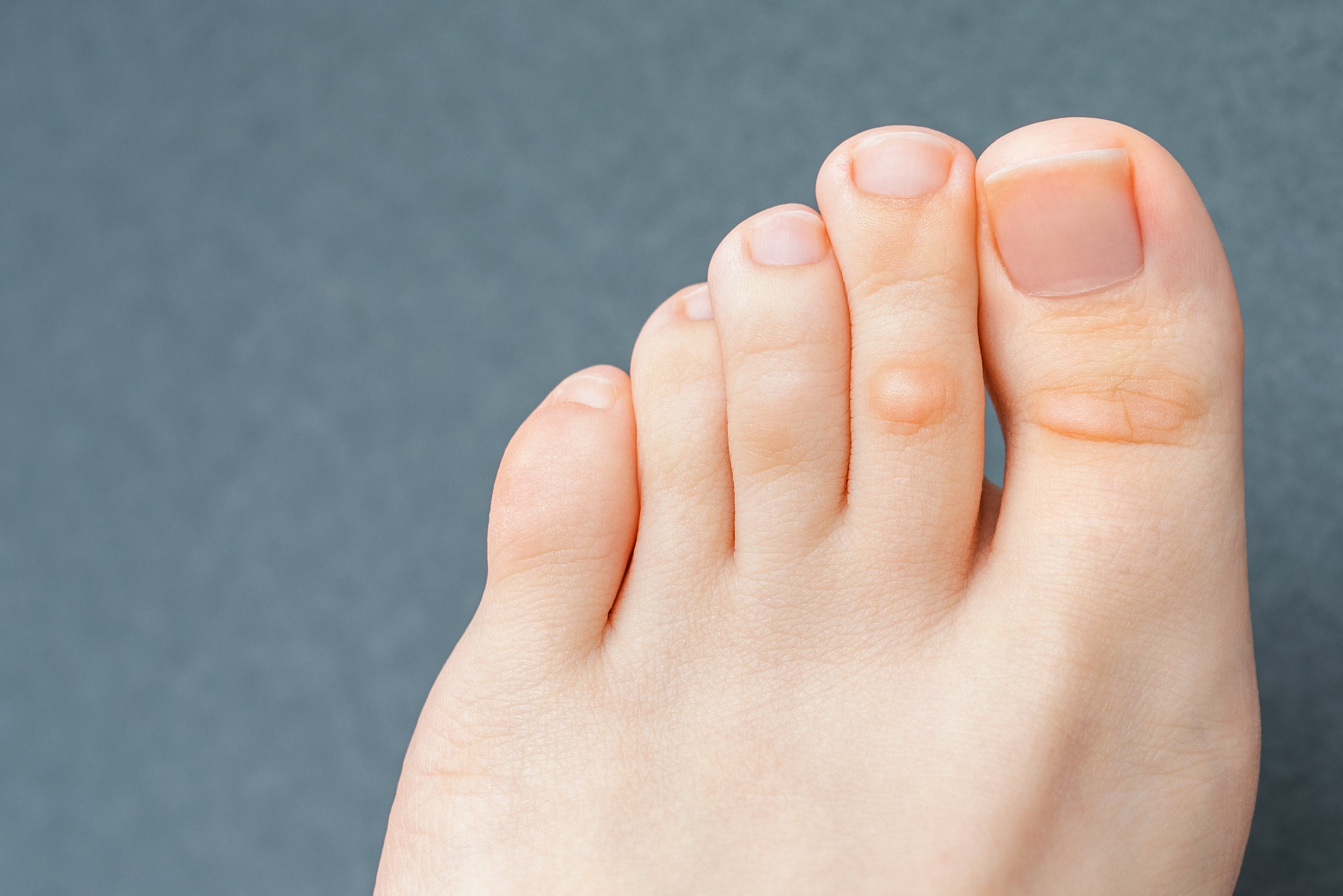
Corns
Corns are small round yellow bumps that develop on the top of your toes and can be very painful. You can tell the difference between a corn and a callus because a corn has a hard center. Corns develop as a result of pressure from another toe or poorly fitting shoes. You can wear corn pads to relieve the pressure, but don’t try to remove a corn yourself. A podiatrist can shave the corn off in a simple procedure and also recommend shoes that will reduce the chance of developing another corn.
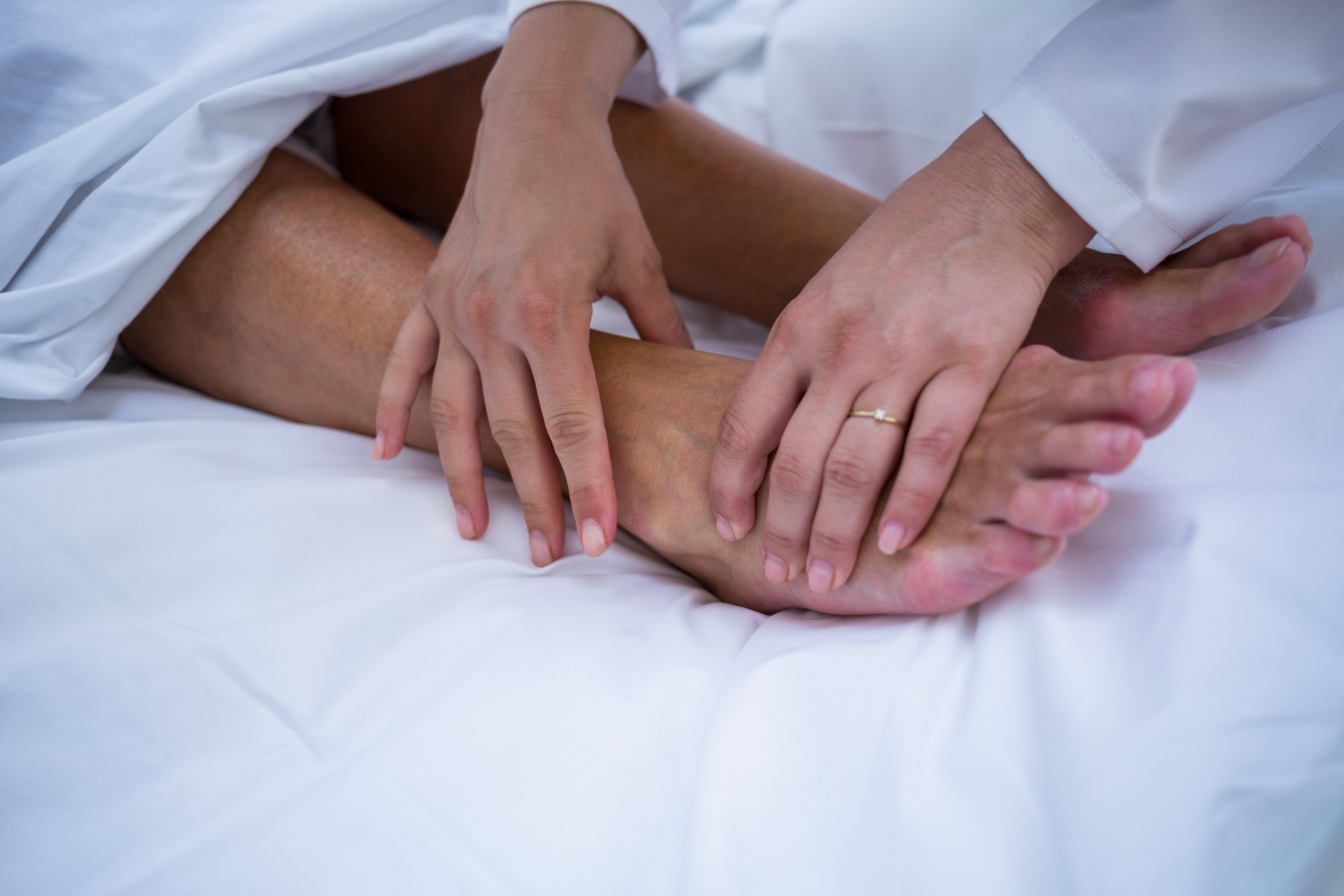
Diabetic foot pain
High blood sugar can damage your nerves, and diabetics are prone to developing neuropathy, or nerve pain, in the feet. It causes tingling, a burning or stinging sensation, or weakness. Diabetics may also develop foot ulcers, often on the bottom of the foot. Since diabetic nerve damage may lead to numbness, you may be unaware of wounds or other foot problems. If you have diabetes, check your feet or have them checked by a podiatrist on a regular basis. Ask your healthcare provider about medications that may relieve neuropathic pain.

Metatarsalgia
Metatarsalgia is a painful inflammation of the ball of the foot, right behind your toes. It may feel like you have a stone in your shoe, and the pain may get worse when you stand, move, or flex your feet. People who do a lot of jumping or running are prone to metatarsalgia, but it can also be due to ill-fitting shoes. Rest and periodic icing should relieve the discomfort. Make sure you wear well-fitting, supportive shoes to prevent a recurrence of this kind of foot pain.

Hammer toes
Hammer toes are toes that have contracted so that they stay bent at the joints. They may be caused by an injury, shoes that are too tight, or an imbalance in the muscles and tendons of your feet that creates stress. Painful corns and calluses are common on hammer toes, which are treated by padding or orthotics, wearing shoes that don’t press down on the toe, and over-the-counter pain medication if needed. In severe cases, surgery can correct a hammer toe.

Achilles tendonitis
The Achilles tendon connects your heel to your calf. It’s the largest tendon in the body and the one that is most commonly injured. Achilles tendonitis (or tendinitis) means the tendon is inflamed, typically from overuse during sports or other intense activity. Symptoms include pain after exercise that get worse, stiffness that eases up when your tendon is gently exercised or stretched, and swelling. Achilles tendonitis usually improves with rest, periodic icing, stretching, over-the-counter pain medication, or orthotic heel lifts. If it doesn’t improve within three months, see a doctor who may recommend a brace or physical therapy.

Foot fractures and sprains
Feet are very complicated structures that undergo a lot of wear and tear. There are 28 foot bones, connected by a complicated system of muscles, nerves, tendons and ligaments, any of which can be injured. Breaks and sprains can have similar symptoms, including pain and difficulty walking. See a doctor for a diagnosis if you have injured your foot, so he or she can treat it properly. With treatment appropriate for the injury, it is less likely to cause problems down the road. A sprain takes about 2 to 4 weeks to heal, and a fracture typically takes 6 to 8 weeks.
- Foot Pain and Problems. Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/foot-pain-and-problems
- Plantar Fasciitis. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/plantar-fasciitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354846
- Metatarsalgia. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/metatarsalgia/symptoms-causes/syc-20354790
- Tendinopathies of the foot and ankle. American Family Physician. https://www.aafp.org/afp/2009/1115/p1107.html
- Why You Shouldn’t Ignore Ball of Foot Pain. Cleveland Clinic. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/why-you-shouldnt-ignore-ball-of-foot-pain/
- Foot Complications. American Diabetes Association. https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/complications/foot-complications